OPERATORS : PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM
Java offers you endless possibilities, thus the use of operators is vast! There are so many of them out there, all doing different things. But for this blog, lets keep it classy and touch on them a bit by highlighting the Pythagorean Theorem. Such a scary name, right? Don’t sweat it though, there’s nothing to fear here.
Pythagorean Theorem
This is a basic geometric law that can be defined as:
In a right angled triangle: the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
It is represented as:
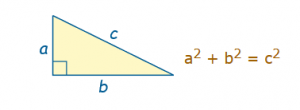
So let’s work on a case problem. Suppose a and c are given as 3 and 5 respectively. What is the value of b ?
Using a2 + b2 = c2 ,
32 + b2 = 52
b2 = 52 – 32
b2 = 16
b = 4
Now to help with this concept, we need to understand some other trigonometric basics. These will be useful in using angles and the sides of the triangle to derive unknowns, given the problem.
SOHCAHTOA
“SOHCAHTOA” is a helpful mnemonic for remembering the definitions of the trigonometric function sine, cosine, and tangent i.e., sine equals opposite over hypotenuse, cosine equals adjacent over hypotenuse, and tangent equals opposite over adjacent,

– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –LIVE A LITTLE:
 – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Having such a math problem we can now proceed to write our java code that solves it using the Pythagorean Theorem and using the trigonometric mnemonic to derive the other two angles of the triangle.
import java.lang.Math;
import static java.lang.Math.acos;
public class Pythagorean {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double height=3, base, hypo=5, angleA, angleB, area, sineA;
base = Math.sqrt((hypo*hypo) – (height*height));
System.out.print(“\n” + “Base = ” + base);
area = (height*base)/2;
System.out.print(“\n” + “Area = ” + area);
sineA = height/hypo;
System.out.print(“\n” + “Sine of angle A = ” + sineA);
angleA = Math.asin(sineA);
angleA = Math.toDegrees(angleA);
System.out.print(“\n” + “Angle A = ” + angleA);
angleB = 180 – (90 + angleA);
System.out.print(“\n” + “Angle B = ” + angleB);
}
}
Explanations:
//declare and initiliaze variables as per the case problem
//using the “=” operator to assign values to the variables
double height=3, base, hypo=5, angleA, angleB, area,sineA;
//find the hypotenus using Pythagorean theorem
//using the “*” operator to multiply values.
//the “\” operator is used alongside “n” to start a new line
//the “+” can be used for addition of values and in this case it is used to add the variable to the output statement.
base = Math.sqrt((hypo*hypo) – (height*height));
System.out.print(“\n” + “Base = ” + base);
//find the area of the triangle using the formula (bh)/2
//the “/” operator is used to divide values or as “//” to indicate comments
area = (height*base)/2;
System.out.print(“\n” + “Area = ” + area);
//Calculating sine of angle using the formula sinx=height/hypotenuse
sineA = height/hypo;
System.out.print(“\n” + “Sine of angle A = ” + sineA);
//to find angle A find the inverse of sineA
angleA = Math.asin(sineA);
angleA = Math.toDegrees(angleA);
System.out.print(“\n” + “Angle A = ” + angleA);
//to find the other angle(B), find the difference between 180 and sum of 90 and angleA
angleB = 180 – (90 + angleA);
System.out.print(“\n” + “Angle B = ” + angleB);
The output is expected to look like this:
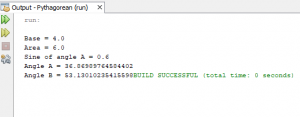
We’re sure that was quite the walk down the memory lane. Now you have some new skills added to you try out some other trigonometric concepts and enjoy the ride.
In summary, working with operators in Java requires one to follow the following steps.
- Understanding the Pythagorean theorem and “SOHCAHTOA” mnemonic to understand operators.
- Using a case problem to illustrate the theories.
- Writing a Java application to solve the case problem
- Explaining the Java code